What is a Heat exchanger?
The heat exchanger is a mechanical device designed to transfer the energy or heat between two working fluids can be gas to liquid (liquid to gas), liquid to liquid, or gas to gas at different temperatures while keeping direct contact or preventing the mixing of the fluids.
By cleverly smartly utilizing this transferred heat (energy), Engineers made some amazing technologies listed below.
- Regenerators
- In Gas power plants, Intercoolers, and Preheaters
- In steam power plants, Boilers, and Condensers
- In HVAC systems, Condensers and Evaporators
- In milk pasteurizing plant, Milk chillers
- Automobiles radiators and Oil coolers
Heat exchangers types
Here, some of the most general heat exchanger types widely used in industries including:
- Shell and tube heat exchanger or Parallel flow heat exchanger
- Plates heat exchanger
- Evaporators, Condensers, and Boilers
Shell and tube heat exchanger or Parallel flow heat exchanger
Shell and tube heat exchangers built from the large cylindrical shell, contain bundles of tubes or series of parallel tubes (sometimes several hundred) fitted in the shell with their axis parallel to the cylindrical shell. That’s why it is also called a parallel flow heat exchanger. The heat transfer starts as one fluid flows inside the tubes and another fluid is forced through the shell that is flowing over, around, and between the tubes within the cylindrical shell. This provides a large surface area for heat transfer. These two integral fluids pathways (Inside the tubes and around the tubes within the shell) are generally built from a high thermal conductive material that permits easy heat transfer.
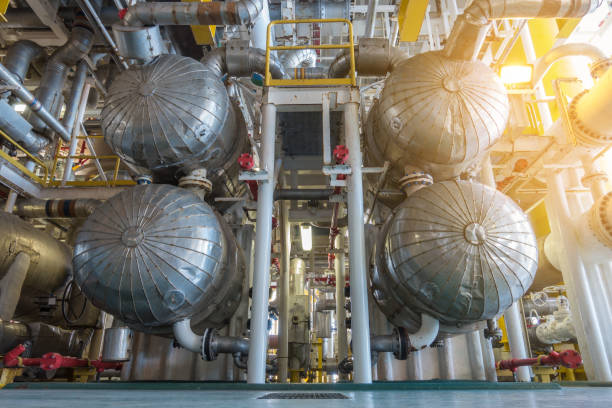

The Shell and tube heat exchanger has a few types based on the number of tubes and the number of shell passes of fluids involved. The tube and shell heat exchanger in which the tubes make one U-turn within the shell is called the “One shell pass and two tube passes” heat exchanger.
Similarly, the tube and shell heat exchanger that consists of four passes in the tubes and two passes within the shell is called a “Two shell pass and four tube passes” heat exchanger.
In tube and shell heat exchanger types, the multi passes of fluid inside the tubes is achieved by forming the multiple U-shape at the end of tubes by bending it and the multi passes of fluid within the shell is achieved by placing the baffles within the shell that forced the shell side fluid across and over the surface of the tubes. By using multiple passes, the heat transfer is excellent due to increased surface area.

People also like : Heat transfer of radiation
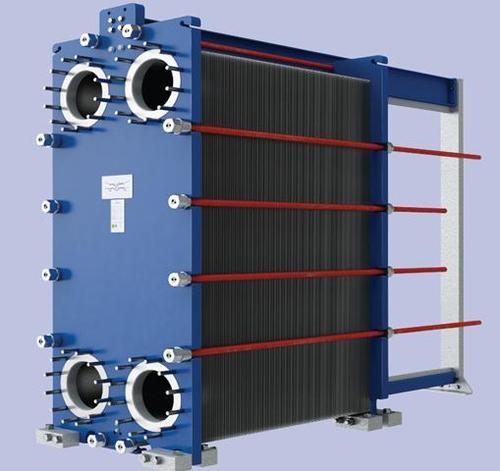
Plates heat exchanger
Plates heat exchanger are made from pairs of high thermal conductive material plates on which corrugations are made. The corrugations create turbulence and increase surface area, both of which maximize the heat transfer rate in a heat exchanger. Each pair of plates forms a flow gap or flow channel through which hot or cold fluid can flow. The pair of plates is known as a plate stack. Every plate stack is held by a tightening bolt in a Plates heat exchanger. In the Plates heat exchanger, the plate stacks are arranged in an alternative manner cold-hot-cold-hot. Plates heat exchanger are widely used for liquid-to-liquid heat transfer.
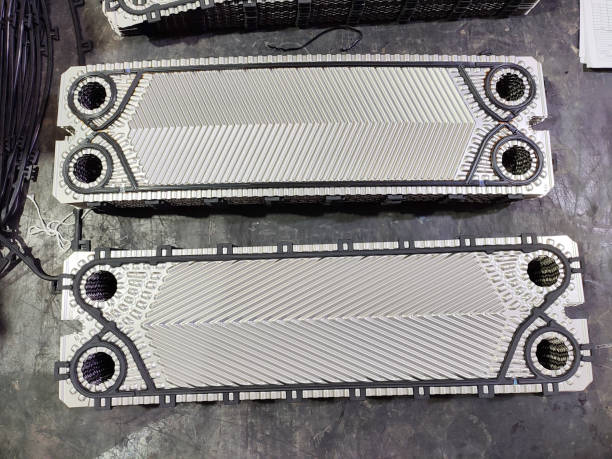
In the Plates heat exchanger, hot fluid enters the Plates heat exchanger through the hot inlet. The gasket directs the hot fluid into the flow channel, but not into the flow channel between the next plate stack. The flow of hot fluid continues so that each alternative set of plates is filled with hot fluid.
Same time, cold fluid enters the Plates heat exchanger through the cold inlet. The gasket directs the cold fluid where no hot fluid is present and plates start to fill with cold fluid.
Now, the plates heat exchanger is full of cold and hot fluid and heat transfer takes place. Note that, two flowing fluids are always adjacent to each other throughout the plates heat exchanger. Both fluids do not mix because they are separated by a gasket from each other.
People also read : What is Thermal Resistance?
Evaporators, Condensers, and Boilers
Evaporators
Evaporators are one kind of heat exchanger used in refrigeration systems. Evaporators are used on the low-pressure side where the liquid refrigerant flows through evaporator tubes.
Evaporator working
The evaporator absorbs heat from the surrounding space (Refrigerator cabin). Note that, the liquid refrigerant has a low temperature compared to the surrounding space temperature. Due to that, According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat flows from the surrounding space (High temperature) to the evaporator tube (Low temperature) and the surrounding space (Refrigerator cabin) become cool (below atmosphere temperature).
Condensers
Condensers are also one kind of heat exchanger used in refrigeration systems. Condensers are used on the high-pressure side where vapor refrigerant flows through condenser tubes.
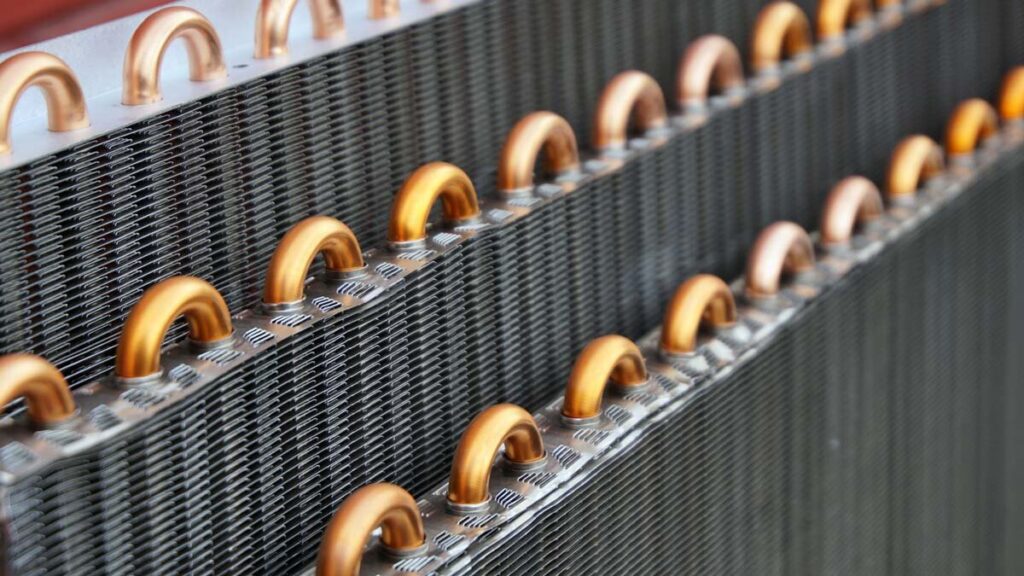
Condensers working
The condensers reject heat from vapor refrigerant. Note that, the vapor refrigerant has a high temperature compared to the surrounding condensing medium (Normally air or water). Due to that, again according to the second law of thermodynamics, heat flows from the vapor refrigerant (High temperature) to the condenser tube (Low temperature) and the vapor refrigerant becomes cool and converted into liquid refrigerant.
Boilers
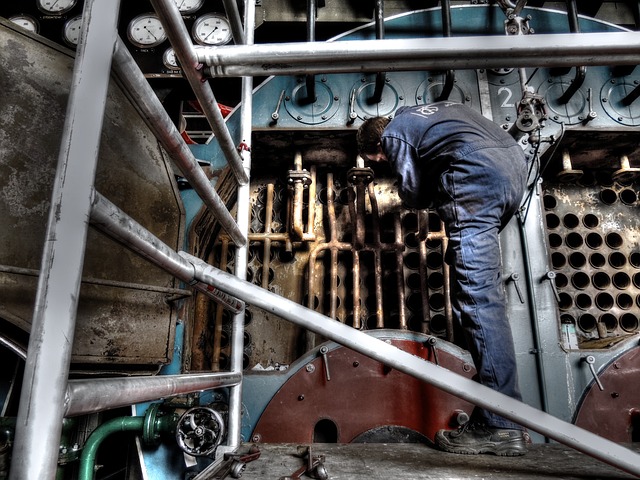

Boilers are also a kind of heat exchanger used in steam power plants to produce steam, in which the freshwater is flowing through the boiler tubes and burning fuel gas passes over the boiler tubes. The heat transfer starts and water is converted into steam.
A heat exchanger that will achieve a specified temperature change in a fluid stream of known mass flow rate use LMTD
To predict the outlet temperatures of the hot and cold fluid streams in a specified heat exchanger. NTU-effectiveness
Analysis and Design of heat exchanger
Whenever an industry needs to purchase or design a heat exchanger, there are several required tasks or parameters that should satisfy the industry standard like..
- For known mass flow rate, select the heat exchanger that will achieve a pre-defined temperature change in fluid stream or…
- For a given or known size of the heat exchanger, determine the outlet temperature of the cold and hot fluid stream.
To solve these two criteria, Engineers designed the heat exchanger and carried out an analysis of it. Generally, there are two methods of analysis and design of heat exchanger.
- Log mean temperature difference (LMTD)
- Effectiveness – NTU method
The LMTD method of analysis and design of the heat exchanger is best suited for the first task. The Effectiveness – NTU method of analysis and design of heat exchanger is best suited for the second task.
Log mean temperature difference (LMTD)
In the heat exchanger, the rate of heat transfer is calculated by,
Q = UAsdT
Here,
U = Overall heat transfer coefficient
As= Surface area of tubes
dT = Temperature difference between cold and hot fluids
Sometimes a situation arises when you need to design or order a heat exchanger according to fix space in which it can be installed properly without compromising the industry requirement like pre-determined (Already known) inlet temperature of hot fluid, the outlet temperature of cold fluid, and heat transfer rate Q.
In this situation, the LMTD (Log mean temperature difference) method of analysis of the heat exchanger is used. In LMTD, the inlet temperature of hot fluid and both the inlet and outlet temperature of cold fluid are known. Also heat transfer rate Q and overall heat transfer coefficient U are known. Based on that parameters, you need to determine the size of the heat exchanger as the surface area can be calculated from the heat transfer rate equation.
Q = UAsdT
In short, LMTD (Log mean temperature difference) method is very suitable for identifying the size of the heat exchanger when the inlet temperature of the hot fluid and both the inlet and outlet temperature of the cold fluid and the mass flow rate are specified.
People also read : what is the characteristic curve or diagram of a centrifugal pump? what do these pump diagrams represent?
Effectiveness – NTU method
Sometimes a situation arises when you need to calculate the rate of heat transfer and outlet temperature of cold and hot fluid. The mass flow rate and heat transfer surface area or the size of heat transfer are known. The ultimate task is to determine the performance of the available heat exchanger.
In this situation, the heat transfer effectiveness of a heat exchanger is used, which excellently made easy heat exchanger analysis. The best feature of the effectiveness of a heat exchanger is, it gives the facility to calculate the heat transfer rate without knowing the outlet temperature of fluids.
The heat transfer effectiveness of a heat exchanger is the ratio of the Actual heat transfer rate to the Maximum possible heat transfer rate.
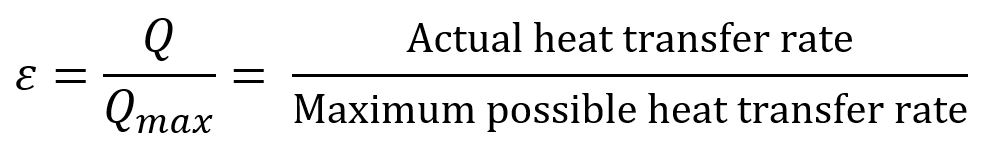
Actual heat transfer rate, Q = mcCpc (Tc, out – Tc, in) = mhCph (Th, in – Tc, in)
Where, Cc = mcCpc and Ch = mhCph are the heat capacity rates of the cold and the hot fluids, respectively.
mc , mh = Mass flow rates
Cpc , Cph = Specific heats
Tc, out , Th, out = Outlet temperatures
Tc, in , Th, in = Inlet temperatures
The heat transfer rate is maximum when there is a maximum temperature difference in the heat exchanger. The maximum temperature difference is the difference between the inlet temperature of cold and hot fluids and the fluid with the smaller heat capacity rate.
Maximum possible heat transfer rate, Qmax = CminTmax = Cmin (Th, in – Tc, in)
The effectiveness relations of a heat exchanger consist of the specific quantity called the Number of transfer units (NTU). The NTU is defined as
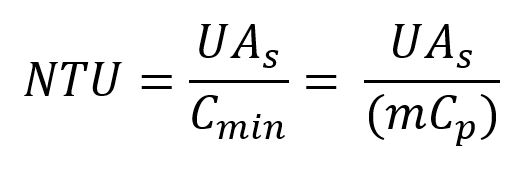
The NTU (Number of transfer units) is proportional to the surface area A. Thus, the larger the NTU, the larger the size of the heat exchanger.
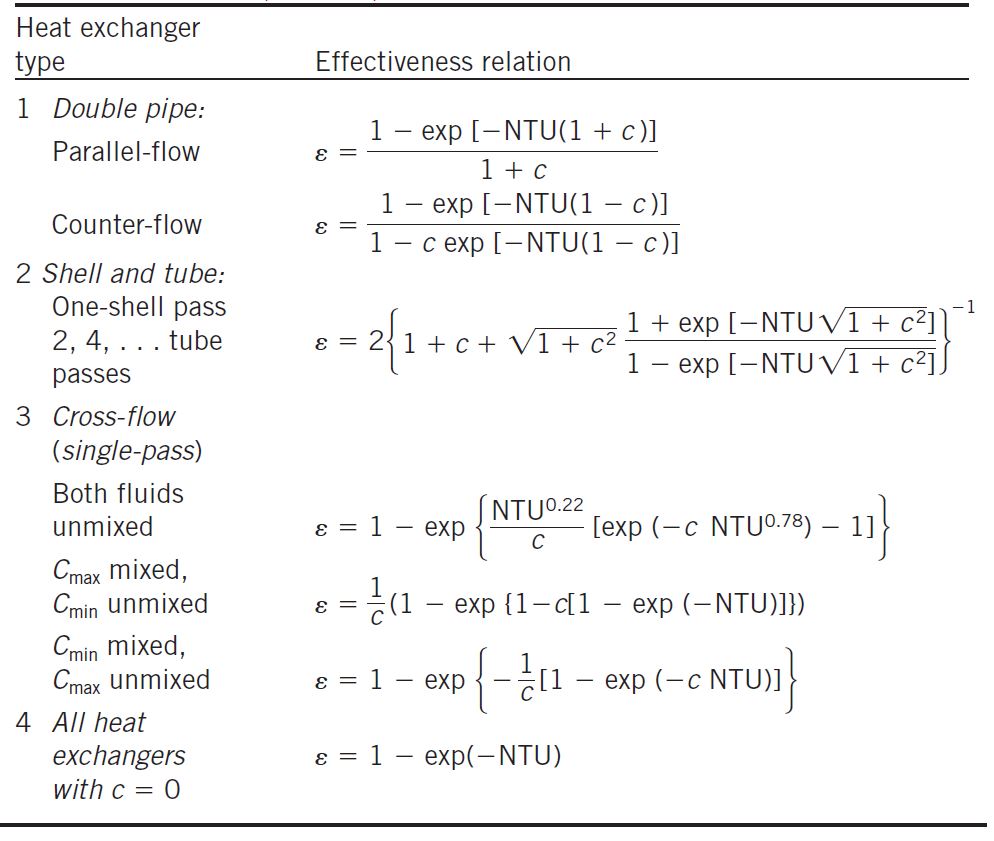
The effectiveness of a heat exchanger depends on the flow pattern as well as the design of heat exchangers. Therefore different types of heat exchanger have different values of effectiveness listed below image.
How to improve the heat transfer rate of the heat exchanger or How to increase the efficiency of the heat exchanger?
Installation – The heat exchanger should be installed according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. The counter flow arrangement is the most efficient flow arrangement in the heat exchanger. Be sure that, the heat exchanger is always full of working fluids.
Flow rate – A greater flow rate will increase the capacity of the heat exchanger to transfer heat.
Increase temperature difference – The temperature difference between hot fluid and cold fluid is very important when designing of the heat exchanger. Larger the temperature difference, effective the heat transfer rate. Because low-temperature fluid extracts more heat from the hot fluid.
Heat exchanger manufacturer in India
Here is the list of some local reputed heat exchanger manufacturers in India
Kinem Engineering Industries
It is a well-experienced heat exchanger manufacturer in India having 40+ years of experience in heat exchanger manufacturing in India established in 1981. The company has manufacturing units in Thane and Bhiwandi, India. The company earned various certificates that indicate the company’s quality and design standards for its products. The company export across 18 countries all over the world. Here is the website kinam.in
Vikrant heat exchanger Pvt Ltd.
It is an experienced heat exchanger manufacturer in India having 27+ years of experience in heat exchanger manufacturing in India. The company export across 25+ countries all over the world. www.vikrantheatexchangers.com
Flowtex Engineers
It is a well-experienced heat exchanger manufacturer in India having a large variety of product ranges. It is established in 2016. It is AN ISO 9001:2015 certified company. The company has its manufacturing unit in Karnataka, India. www.flowtexheatexchangers.com
United heat exchanger
The company was established in 1980. The company has rich experience in heat exchanger manufacturing in India having 30+ years of experience in this business. The company has a wide product portfolio range. Company production unit located in Tamilnadu, India. www.unitedheatexchangers.com
Techpert process
This heat exchanger manufacturer in India was established in 2013, The Company has expertise in the manufacturing of Evaporator. The company has its manufacturing unit in Pune, India.
Radiant Group
Established in 1977, it is a well-experienced heat exchanger manufacturer in India having a large variety of product ranges. The company has its manufacturing unit in Pune, India. www.radiantengineers.com
Artson Engineering Limited (A subsidiary of TATA project limited)
The company has a manufacturing units in Powai, Nashik, and Nagpur, India. artson.net
Other well-known Heat exchanger manufacturers in India
- Centpro (Pune)
- Plateheatexchanger.co.in (UP)
graef m 20 bronze schwimmabzeichen bedingungen air presto fly se smartwatch mit höhenmesser und gps testberichte elektrische zahnbürsten תנור indesot brother lc 3211 multipack rock radio słuchaj online accesorios nevera siemens seiko 5 automatic snzg13k1 westfield campingstuhl tasche 4 chapeaux bruleurs brandt tabouret de bar scandinave tournant miele tiefkühler gay adult cam

